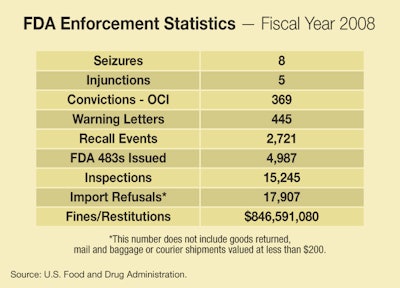
NEW UPDATED FDA ENFORCEMENT STATISTICS: New, updated FDA enforcement statistics, now including data for fiscal 2008, are posted below with new graphics added June 2, 2009. This data includes trends back to 2000 for FDA inspections, warning letters, seizures, injunctions, criminal prosecutions, and other actions. It updates information included in April's The Legal Side column by our legal editor, Eric Greenberg.
It’s generally the case that examining the numbers of FDA inspections,
Warning Letters, seizures, injunctions, prosecutions, import refusals,
and recalls can leave one confused about whether the consumer
protection agency is being busy or sleepy, aggressive or lax.
It’s also the case, admittedly, that for any individual packager in an
FDA-regulated business (food, drug, medical device, cosmetic, animal
food and drug, biological products, radiological products), the
statistics are just about meaningless if your company is the subject of
a particular enforcement action. Still, it can be useful to put your
particular issues into some context, and that is the goal of examining
these statistics.
Finally, it’s also quite obviously the case that one high-profile
outbreak, like the recent substantial headaches with peanut
butter-containing foods made by Georgia’s Peanut Corporation of
America, gives many people the impression that FDA is being lax in
oversight and enforcement. That conclusion is not necessarily warranted
from the limited fact of one incident, although it was a big one. But
when members of Congress are among those getting that troubling
impression, the result can be new legislation giving FDA new powers to
regulate.
Surrounding you here are data on FDA’s enforcement actions during 2007,
and charts showing the trends in past years and up through 2007. Here
are a few observations:
• It’s useful to start by examining the raw numbers for fiscal 2007.
The numbers of Injunction and Seizure actions, as is typical, are
modest. FDA simply never brings too many of these. FDA quite commonly
raises the specter of being the subject of one of these serious actions
to pressure a company to recall a product or to agree to a Consent
Decree that may contain a variety of provisions (such as agreed
financial penalties, agreements to shape up compliance practices, and
so on).
• The raw number for “Convictions—OCI”, meaning criminal actions under
the auspices of FDA’s Office of Criminal Investigations, is a
surprisingly high 344. It’s not clear who all these criminal defendants
were, and FDA isn’t immediately forthcoming with background on that
figure, though it’s known that those cases include actions against
sellers of counterfeit drugs over the Internet and otherwise, and
against those who illegally promote the sale of prescription drugs.
• FDA inspections are typically the starting point for the sequence of
enforcement actions, since serious violations discovered at inspections
will often result in Warning Letters, which in turn, if not properly
responded to, can turn into seizures, injunctions, prosecutions, or
recalls or consent decrees. So you can look at the number of
inspections as one indicator of how aggressive FDA is being regarding
enforcement. The number of inspections was down in 2007 over prior
years, which is consistent with the pattern going back to 2003.
• And if Warning Letters are the most common follow-up to an inspection
that uncovers problems, those are down, too, and have been going down
since at least all the way back in 2000, interrupted by a spike in
2004.
• Recalls have been generally on the upswing since 2000, which may mean
FDA’s pressure is getting through to companies with product problems,
or may mean companies are voluntarily recalling more frequently.
Remember, almost all recalls are voluntary on the part of the
manufacturer or distributor, though as noted are often undertaken under
pressure of serious action by FDA. Exceptions are medical devices,
human tissue products, and infant formula. FDA can order recalls of
those types of products in appropriate circumstances. (The data charts
don’t reveal how many recalls were voluntary and how many were not.)
• Import refusals, in which FDA turns away suspected violative products
at the border, are up up up in the 2000’s, though they have leveled off
in the past 2 years.
We like to check in on the FDA enforcement stats in this space with
some regularity, trying to discern patterns. Looking ahead, if Congress
is serious about even some of the various proposals now under
consideration to add FDA funding and powers, including the power to
order recalls, and if FDA takes that change in the law as marching
orders to become more active on the enforcement front, then we can
expect packagers and others in FDA-regulated businesses to be under
increased pressure and scrutiny from the agency. And, we can expect
these figures to rise consistently in coming years.
Eric can be reached at [email protected], and visit his firm’s Web
site at www.ericfgreenbergpc.com.