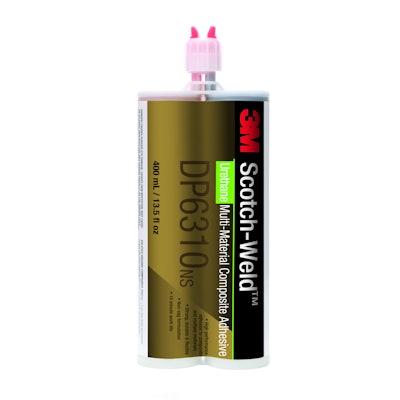
More design engineers are relying on composite substrates to reduce costs and increase lightweighting possibilities in assembly. Compared to adhesives, traditional mechanical fasteners are not effective with these materials because of their fatigue limited stress absorption, and in many cases, engineers make sacrifices to accommodate the restricted capabilities of a mechanical fastener. With the design engineer in mind, 3M introduces Scotch-Weld Multi-Material Composite Urethane Adhesives DP6310NS and DP6330NS to its portfolio of structural adhesives.
3M™ Scotch-Weld Multi-Material Composite Urethane Adhesives were engineered to create durable bonds with minimal surface prep, between medium to high energy surfaces like carbon fiber, fiberglass, reinforced plastics, and painted or unpainted metal. The fast and robust bonding power of these adhesives opens the door for design engineers to explore new options. Tough, long-lasting bonds for dissimilar materials require products that are highly energy-absorbing. The moduli of these adhesives were formulated to provide high strength and durability for bonding composites to metals.
Drilling holes in a plastic substrate for a screw or bolt can lead to cracking and other premature failures. Adhesives maintain structural integrity and provide secure bonds across diverse metals, plastics and composites. Incorporating adhesives into automotive assemblies is an easy way to eliminate added weight from mechanical fasteners. Structural adhesives also improve the aesthetic finish of a design, while reducing the installation time and costs that accompany traditional joining methods.
“We see the use of composite materials in design as a growing trend, but often assembling these materials with mechanical fasteners is not efficient, economical or aesthetically-pleasing,” says Chris Enstrom, Marketing Manager for structural adhesives at 3M. “The broad applicability of 3M Scotch-Weld Multi-Material Composite Urethane Adhesives makes them the new standard go-to products when it comes to composite bonding, especially within the transportation and sporting goods industries.”
The 3M Scotch-Weld Multi-Material Composite Urethane Adhesives are available in two versions with varying handling times to fit the scope of assembly. The 10-minute work life version is ideal for a speedy, targeted application, with declamp time of approximately 45 minutes. The 30-minute work life version, followed by a two-hour clamp time, is designed with a large surface application in mind. The extended cure time allows the user more time to work with the product and ensure a secure bond. Both the 10- and 30-minute work life versions can generally be used without a primer, expediting the application process.